About This Brief
Question 1
Listen to the briefing note The Briefing Room Explainer: What is a Tariff?(available here https://www.bbc.co.uk/sounds/play/p0klnnm6 ).
Focusing particularly on the first 8 minutes, provide a brief overview of the key points that are made about the impacts of tariffs, using appropriate figures where they will aid the explanation.
Question 2
Consider the following data which shows the input requirements to produce two goods (wine and cheese) using two factors (capital and labor).
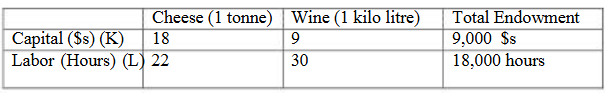
Assuming that the resource constraints can be represented with the following general equations
aKCQC + aKWQW = K
aLCQC + aLWQW = L
aKC ≡unit capital requirement in cheese
aKW ≡ unit capital requirement in wine
aLC ≡ unit labor requirement in cheese
aLW ≡unit labor requirement in wine
L ≡ Laborendowment
K ≡Capital endowment
- Solve for the equilibrium output levels of wine and cheese.
- Suppose the labor endowment falls from 18,000 hours to 15,000 hours. Solve for the new equilibrium output levels of wine and cheese.
- Identify which good is labor intensive and which is capital intensive.
- Which theorem is implied by the results and why?
Question 3
(a)Assume Japan’s supply (S) and demand (D) for beef is represented by the following equations where P is domestic price per tonne, and quantities are in tonnes:
DJ = 650 – 20P
SJ = 100 + 30P
Now consider Australia, an exporter of beef, with the following demand and supply functions
DA = 150 – 5P
SA = 50 + 30P
- Derive Japan’s import demand function.
- Derive Australia’s export supply function.
- Assuming bilateral trade between the two countries identify the world price and the quantity traded.
(b) If there were a trade war between the two countries, and all trade were banned
- Derive the price and quantity produced in each country.
(c) Suppose that there is a resumption of trade, but Japan decides to limit beef imports from Australia by imposing an import tariff of $1. Calculate the effect of the tariff on:
- The price of beef in each country
- The quantity of beef supplied and demanded in each country and
- The volume of trade
- Use graphical analysis to illustrate the impact of the import tariff on the welfare of Japans consumers, producers, and government.
Question 4
Vietnam is a small country that cannot affect world prices of potatoes in the international market (its imports represent about 2% of all trade in potatoes). Assume that Vietnam imports potatoes from the international market at a world price (Pw) of 10 dollar per kilogram.
The domestic supply and demand curves (with quantity measured in millions of kilos) for potatoes in Vietnam are:
Qs = -1 + 1.5P
Qd = 80-1P
(a)
- What is the equilibrium price in autarky (no trade)?
- What is the quantity produced and consumed in autarky?
- Derive the import demand function for potatoes
- What is the quantity produced and consumed with trade?
- What is the quantity imported?
(b) Now consider the effect of an import quota of 20m kilos:
- What happens to the price of potatoes and quantity consumed?
- How much is produced domestically and how much is imported?
(c) Compute the following welfare changes after the import quota is imposed on:
- Consumer surplus
- Domestic producer surplus
- Who else might gain, and under what circumstances?
(d) Provide a graphical analysis of (a) (b) and (c). You do not have to draw the graph to scale